Navigation Menu
Contact Us
- Email:
- info@wxavatar.com
- Address:
- Yurong Village, Yuqi Street, Huishan District, Wuxi, China.
Release Date:Feb 22, 2025 Visit:21 Source:Roll Forming Machine Factory
Cold forming is a highly efficient manufacturing process that shapes metal at room temperature without the need for heating. This method is widely used across industries to produce strong, precise, and cost-effective components. By applying mechanical force to metal, cold forming alters its shape while enhancing its mechanical properties, making it a preferred choice for many applications.
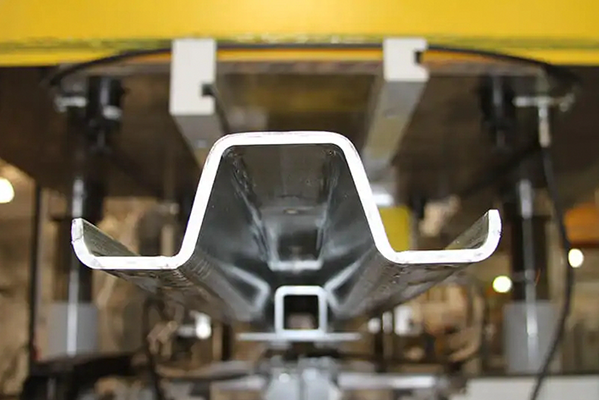
The Cold Forming Process
Cold forming works by subjecting metal to high pressure, typically using dies and punches, to reshape it into desired geometries. The process begins with a metal blank, usually a wire, rod, or strip, which is fed into a cold forming machine. The machine then applies force to deform the metal, creating complex shapes with high accuracy. Common cold forming techniques include cold rolling, cold forging, extrusion, and stamping.
One of the key advantages of cold forming is its ability to improve the strength and durability of the metal. As the metal is deformed, its grain structure becomes denser, resulting in enhanced mechanical properties such as increased hardness and tensile strength. This makes cold-formed components ideal for applications requiring high performance and reliability.
Applications of Cold Forming
Cold forming is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics. In the automotive sector, it is employed to produce critical components like bolts, screws, and gears. These parts benefit from the superior strength and precision that cold forming provides, ensuring they can withstand the demanding conditions of vehicle operation.
In the aerospace industry, cold forming is used to manufacture lightweight yet robust components, such as fasteners and structural elements. The process's ability to work with high-strength alloys makes it indispensable for meeting the stringent safety and performance standards of aerospace applications.
The construction industry also relies heavily on cold forming to produce steel beams, frames, and other structural components. Cold-formed steel is known for its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it a popular choice for modern building projects. Additionally, cold forming is used in the production of electrical connectors, terminals, and other small parts in the electronics industry, where precision and consistency are paramount.
Advantages of Cold Forming
Cold forming offers several benefits over traditional hot forming methods. First, it eliminates the need for heating, reducing energy consumption and production costs. Second, it produces less material waste, as the process is highly efficient and generates minimal scrap. Third, cold-formed components often require little to no additional machining, further reducing production time and expenses.
Moreover, cold forming enhances the surface finish of the metal, resulting in smoother and more aesthetically pleasing products. This is particularly important for components that are visible or require a high level of precision.
The Future of Cold Forming
As technology advances, cold forming continues to evolve. Innovations in materials science and manufacturing equipment are expanding the capabilities of the process, enabling the production of even more complex and high-performance components. With its ability to deliver cost-effective, sustainable, and high-quality solutions, cold forming is poised to remain a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
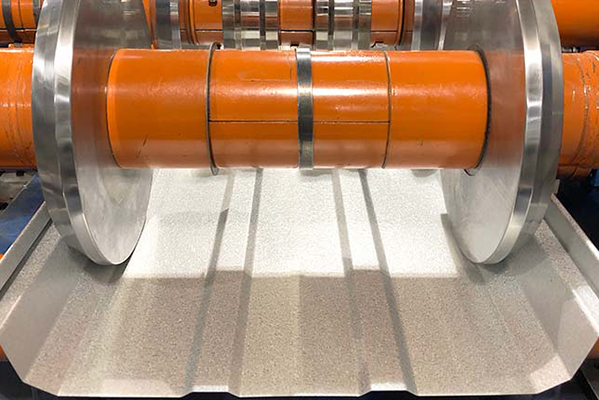

In conclusion, cold forming is a transformative process that shapes metal at room temperature, offering numerous advantages in terms of strength, precision, and efficiency. From automotive and aerospace to construction and electronics, the applications of cold forming are vast and continually growing. As industries strive for greater innovation and sustainability, cold forming will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of manufacturing.