Navigation Menu
Contact Us
- Email:
- info@wxavatar.com
- Address:
- Yurong Village, Yuqi Street, Huishan District, Wuxi, China.
Release Date:Apr 15, 2025 Visit:4 Source:Roll Forming Machine Factory
Rolling is a fundamental metal forming process that shapes metal by passing it through rotating rollers. This method is widely used in manufacturing to alter the thickness, width, or surface finish of metal workpieces. As a primary industrial operation, rolling plays a significant role in producing various metal products.
Definition and Characteristics
Rolling is classified as a metal forming process because it permanently deforms metal through compressive forces without removing material. The process involves:
Material Preservation: Maintains the original volume of metal while changing its shape
Plastic Deformation: Causes permanent structural changes in the metal
Dimensional Control: Precisely modifies thickness and surface characteristics
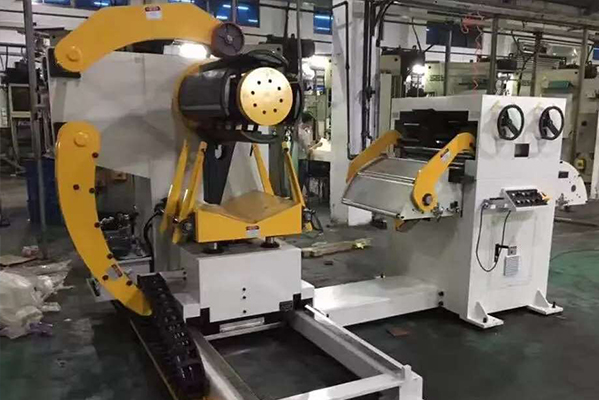

Types of Rolling Processes
1. Flat Rolling
Reduces thickness of rectangular cross-sections
Produces sheet metal and plates
Can be performed hot (above recrystallization temperature) or cold (room temperature)
2. Shape Rolling
Forms metal into specific cross-sectional profiles
Creates structural shapes like I-beams, rails, and channels
Uses specially contoured rollers
3. Ring Rolling
Expands diameter of ring-shaped workpieces
Maintains or reduces wall thickness
Produces seamless rings for bearings and turbines
Industrial Applications
Rolling serves as a critical manufacturing step for:
Construction Materials: Structural beams, reinforcement bars
Transportation Components: Railroad tracks, automotive body panels
Consumer Goods: Appliances, packaging materials
Advantages of Rolling
High Production Efficiency: Continuous processing of long workpieces
Material Property Enhancement: Improves grain structure and mechanical properties
Surface Quality Improvement: Produces smooth finishes on final products
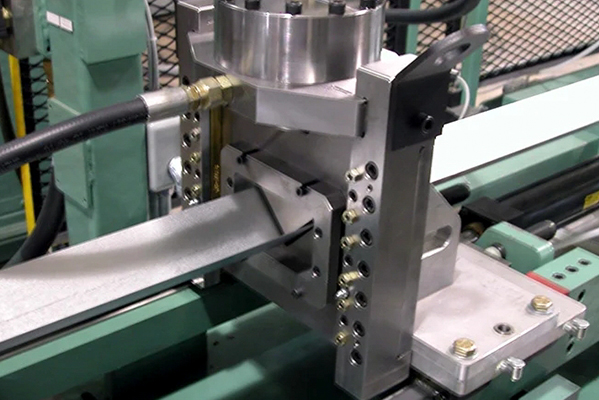
Conclusion
Rolling is indeed a vital metal forming process that transforms raw metal into usable forms through controlled deformation. Its versatility in producing both simple and complex shapes makes it indispensable in modern manufacturing. The process's ability to maintain material integrity while achieving precise dimensional control confirms its classification as a true metal forming method.